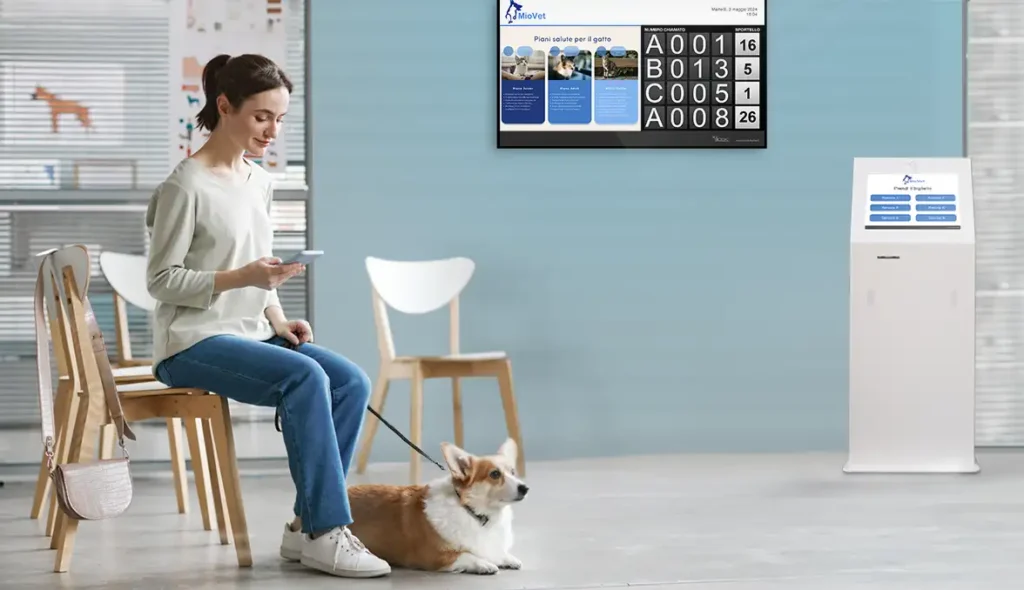
Queue management represents a crucial area of study and application that focuses on optimizing waiting flows in various contexts and sectors.
At its heart, queue management is about organizing and controlling waiting lines, whether they are people waiting to receive a service, objects to be processed, or data waiting to be transmitted.
The main objective is to reduce waiting times, improve the efficiency of services and increase the satisfaction of the users or customers involved.
1. The concept of queue management
Queue management uses mathematical principles and statistics to analyze and predict traffic and wait flows, allowing organizations to optimize resources and improve operations.
Through the use of queuing models, companies can simulate various waiting scenarios and determine the most efficient configuration to minimize waiting times and maximize service capacity.
Importance of queue management in different sectors
Queue management finds application in a wide range of industries, each with its own specifics and challenges.
- Retail: In the retail sector, effective queue management can mean the difference between a satisfied and dissatisfied customer. Strategies such as express checkouts for smaller purchases or virtual queue systems improve the shopping experience, reducing the perception of waiting and encouraging customer returns.
- Healthcare: In the healthcare industry, effective queue management is not just a matter of patient satisfaction, but can also have direct health implications. Prioritization of cases based on urgency, online bookings and electronic triage systems are essential to ensure patients receive the care they need in a timely manner.
- Banks and Financial Institutions: Banks use queue management systems to reduce waiting times in branches, improve staff efficiency and offer a more pleasant customer experience. Solutions such as booked appointments and digital banking services help optimize customer flows.
- Customer Support: In customer support, whether call centers or online help desks, efficient queue management is critical to maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction. The use of ticketing software, chatbots and predictive analytics helps manage requests efficiently, ensuring customers are attended to quickly.
Queue management, therefore, proves to be a key element not only for improving operational efficiency, but also for enhancing the customer experience, positively influencing the perception of the service offered and customer loyalty.
An organization’s ability to effectively manage queues can therefore become a significant competitive advantage, differentiating it from competitors and contributing to its long-term success.
2. Queuing Theory
Queuing theory is a branch of mathematics that studies the arrival of customers (be they people, workpieces, data, etc.) at a certain service, their waiting in the queue and their subsequent service.
This field uses mathematical models and statistics to analyze and predict the behavior of waiting systems, allowing you to optimize the use of resources and improve operational efficiency.
Overview of Queuing Theory
Usually considered a branch of operations research, queuing theory was first formalized in the 1900s by Agner Krarup Erlang to address congestion problems in telephone networks.
Since then, it has evolved to apply to a wide range of contexts, from computer network design to airport management, from industrial manufacturing to the service sector.
The main elements analyzed in a queue model are:a
- Arrivals: The process that describes how and when customers arrive at the queue system.
- Service: The mechanism through which customers are served.
- Number of Servers: The number of available service channels.
- System Capacity: The maximum number of customers that can be present in the system at one time.
- Queuing Discipline: The order in which customers are served (e.g., first come, first served).
Main Queue Models
There are several tail designs, each suited to specific situations. Among the best known are:
- M/M/1 Model: A basic model with a single server, arrivals and service times that follow an exponential distribution.
- M/M/c Model: Similar to M/M/1, but with multiple servers, useful for analyzing situations with multiple service channels.
- M/G/1 Model: A model that allows service times with a generic distribution, providing greater flexibility in service modeling.
Prediction of the behavior of waiting systems
Queuing theory allows us to predict various aspects of waiting systems, such as:
- Waiting Times: The average time a customer spends in queue before being served.
- Queue Length: The average number of customers queuing at any given time.
- Resource Utilization: The percentage of time servers are busy.
Using these models, organizations can simulate the impact of system changes, such as adding servers or changing queuing discipline, to identify solutions that minimize wait times and maximize efficiency.
Queuing theory thus offers powerful tools for analyzing and improving waiting systems in numerous areas, significantly contributing to user satisfaction and operational efficiency.
3. Main Queue Management Methodologies
Effective queue management requires the adoption of methodologies and tools that optimize customer flow and reduce waiting times, thus improving user experience and operational efficiency.
Three fundamental strategies in this area are the use of virtual and physical queue systems, the implementation of software for managing reservations and waits, and the application of triage principles for customer prioritization.
Virtual Queuing Systems vs. Physicists
Physical Queuing Systems
Traditionally, physical queuing systems require the customer to be present in a specific location, such as queuing at a store or bank. While simple to implement, they can lead to long wait times and customer dissatisfaction, especially during busy periods.
Virtual Queuing Systems
Virtual queuing systems allow customers to register in a queue without being physically present, using mobile devices or self-service terminals. These systems notify customers of their turn or any delays via SMS, apps or digital displays, allowing them to use their waiting time more productively.
The virtual queue improves the customer experience, reducing the perception of waiting time and increasing satisfaction.
Use of Apps and Software for Reservation and Wait Management
The adoption of dedicated apps and software is essential to manage reservations and waiting lists efficiently.
These tools allow customers to book appointments or services in advance, reducing overload and evenly distributing the workload between different times of the day.
Common features include:
- Online bookings from smartphone or computer.
- Real-time updates on the queue situation.
- Wait time estimates based on predictive analytics.
- Automatic notifications to remind users of their appointments.
These systems not only improve the customer experience but also offer managers tools to monitor demand in real time, optimize resources and predict peak traffic.
Triage principles for prioritizing customers
Triage, a concept originally developed in the medical field, refers to the practice of evaluating and prioritizing cases based on their urgency.
Applied to queue management, triage helps identify and serve customers with the most critical needs first, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently. This can be achieved through:
- Predefined criteria to identify priorities (for example, elderly, pregnant women, emergency cases).
- Analysis of customer data at check-in to determine priority.
- Real-time feedback from field staff for dynamic adjustments.
Implementing these principles into your queue management system not only improves service efficiency but also ensures fair and sensitive treatment of customers, further raising the perception of the quality of the service offered.
In conclusion, the combination of these methodologies – the adoption of virtual queue systems, the use of advanced software for booking management, and the application of triage principles for customer prioritization – represents an overall strategy to address effectively address queue management challenges in a variety of operational contexts.

4. Emerging Technologies in Queue Management
Emerging technologies, in particular artificial intelligence (AI) and predictive analytics, are revolutionizing queue management, offering innovative solutions to optimize waiting flows and improve user experience.
These technologies allow companies to more accurately predict peak traffic, personalize the customer experience and optimize available resources.
Artificial Intelligence in queue management
The AI applied to queue management uses machine learning algorithms to analyze historical and real-time attendance patterns, allowing traffic volumes and waiting times to be predicted with unprecedented precision.
This allows you to:
- Optimize resource allocation: Predicting periods of high demand allows you to allocate staff and resources more efficiently, reducing operating costs and improving service.
- Personalize the customer experience: AI can analyze customer data to offer personalized services, such as suggestions for less crowded times or optimized routes within a store.
Predictive Analysis
Predictive analytics relies on the use of data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning techniques to identify the probability of future events based on historical data.
In the context of queue management, this means:
- Forecasting peak attendance: Analyze trends and historical data to predict periods of greatest attendance, allowing for better planning of staff and resources.
- Estimated waiting times: Provide accurate wait time estimates to customers, improving customer satisfaction and reducing waiting frustration.
Examples of successful technology implementation
Airports
Some airports have implemented AI-based systems to manage passenger flows, using sensors and cameras to monitor queues in real time and optimize staffing at security checks. This has led to a significant reduction in waiting times.
Retail
Large retail chains use predictive analytics to manage checkout lines, analyzing sales data in real time to predict peak traffic and open new checkout lines before lines get too long.
Healthcare
Hospitals and clinics are adopting AI-powered booking systems that optimize appointments based on service time predictions and patient prioritization, improving efficiency and reducing wait times.
These examples demonstrate how artificial intelligence and predictive analytics are transforming queue management, offering solutions that improve both operational efficiency and customer experience.
As these technologies continue to evolve, we are likely to see further innovations and applications in this field, making queue management increasingly efficient and personalized.
5. Case Study: Improvements in customer experience and operational efficiency
Case Study: Implementation of the Virtual Queuing System in a Hospital
Situation
A large hospital has introduced a virtual queue system to manage the influx of patients in the emergency department.
The system allows patients to register online and receive an estimate of the wait time before physically showing up.
Results
The introduction of the system led to a 30% reduction in waiting times, significantly improving patient satisfaction. Furthermore, it allowed healthcare personnel to anticipate their workload, optimizing resource management.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
- Proactively communicating wait times can reduce stress and improve the overall patient experience.
- Analyzing the data collected by the virtual queue system can provide valuable insights for further operational improvements.
6. Strategies to improve customer satisfaction
Strategies to improve customer satisfaction while waiting in queues are crucial, especially in contexts where waiting time can significantly influence the overall customer experience.
Here are some effective tactics:
Effective communication while waiting
Transparency about waiting times and the causes of delays can significantly improve the perception of the service. Implementing information displays, voice announcements or mobile app updates can keep customers informed and reduce frustration.
Creation of comfortable waiting environments
Well-designed waiting environments that offer conveniences such as comfortable seating, access to free Wi-Fi and entertainment can transform waiting into a more pleasant experience. This not only improves customer satisfaction but can also increase the perception of service quality.
Queue management systems
Implement systems such as Kiosk Hydra for the generation of numbered tickets or apps for managing reservations that allow customers to monitor their shift without having to physically stand in queues.
Customer feedback for continuous improvements
Encouraging customers to share their waiting experience provides valuable data for continuous improvement. Feedback can be collected via online surveys, on-site feedback stations or mobile apps or instant survey systems such as Kiosk Emoticon.
7. Queue Management Challenges
The main challenges in queue management include accurately forecasting demand, managing unexpected peaks in crowds and optimizing resources to ensure efficient service without oversizing.
Strategies for dealing with high-density situations and traffic peaks
Use of Predictive Technologies: The use of predictive analytics software can help predict peak attendance and plan accordingly.
Resource Flexibility: Having a system that allows for quick reaction to changes in demand, such as part-time staff or flexible working hours, can help manage sudden peaks.
Alternative Service Channels: Offering customers alternatives to the physical queue, such as online appointments, self-check-ins or digital services, can effectively redistribute the workload.
Addressing queue management challenges requires a holistic approach that integrates advanced technologies, customer feedback and flexible operational strategies.
Through the application of these strategies, organizations can not only improve operational efficiency but also significantly elevate the customer experience.
Conclusions
In conclusion, effective queue management is critical to improving operational efficiency and customer satisfaction in a variety of industries. With the advancement of technologies and the implementation of systems based on artificial intelligence and predictive analytics, organizations can now more effectively address the challenges related to long waits and customer flows.
If your company or institution is looking for an advanced solution that can transform queue management and optimize customer flows, we invite you to consider Kiosk Hydra.
This advanced cloud platform offers innovative features for flow management, suitable for different types of markets.
Whether you manage a single location or a multi-location organization, Kiosk Hydra can help you improve efficiency, reduce wait times and increase your customer satisfaction.
 | Do you want to improve your public service points?Learn more about how Kiosk Hydra can revolutionize queue management in your organization. Don’t let long lines be the only memory your customers take home. |
 |
Do you want to improve your public service points?Learn more about how Kiosk Hydra can revolutionize queue management in your organization. Don’t let long lines be the only memory your customers take home.
|